[Data Science] Use of Series.apply() and DataFrame.apply() functions of the pandas library
Many times when we are processing 2-D tabular data, we wish to add new columns or rows into the table based on some criteria. Python package named pandas is useful for such kind of procesing which has many useful classes and functions. In this blogpost, we will see the use of apply() function defined in the pandas.Series and pandas.DataFrame classes of pandas library.
Problem Statement: We have 2-D tabular data for 70 students, where first column is “ID Name” of the students. The remaining columns are tasks which they have to complete. There are 12 such columns thus size of the table is $70 \times 13$. The task column entries are either “Completed” or “Not completed” depending on whether the task was completed or not. Here, we wish to accomplish following things:
-
Split first column into two namely “ID” and “Name”
-
add two columns namely “Number of tasks completed” and ‘‘Number of tasks pending’’ showing how many tasks a student has completed and how many are remaining, respectively.
Let us solve this problem..
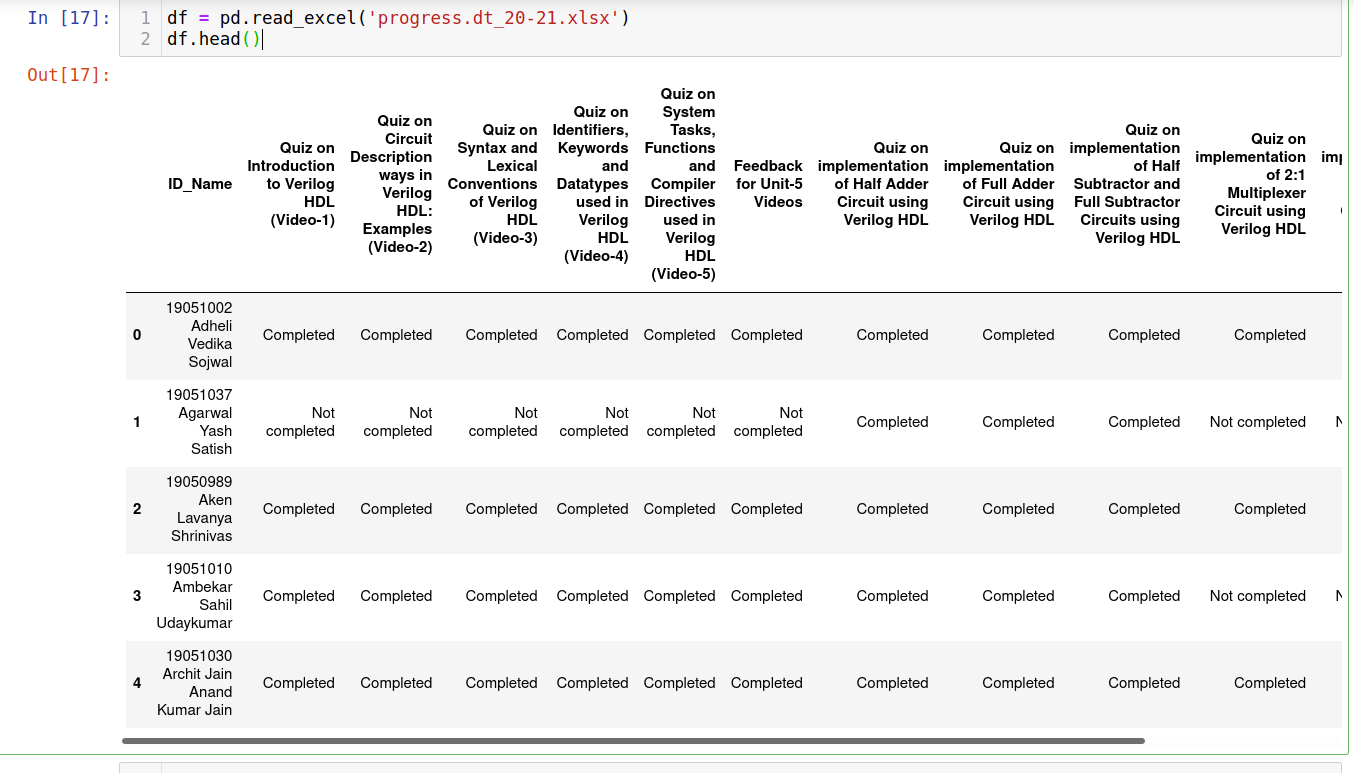
First, we will load and take a look at our tabular data using following code:
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_excel('progress.dt_20-21.xlsx')
df.head()
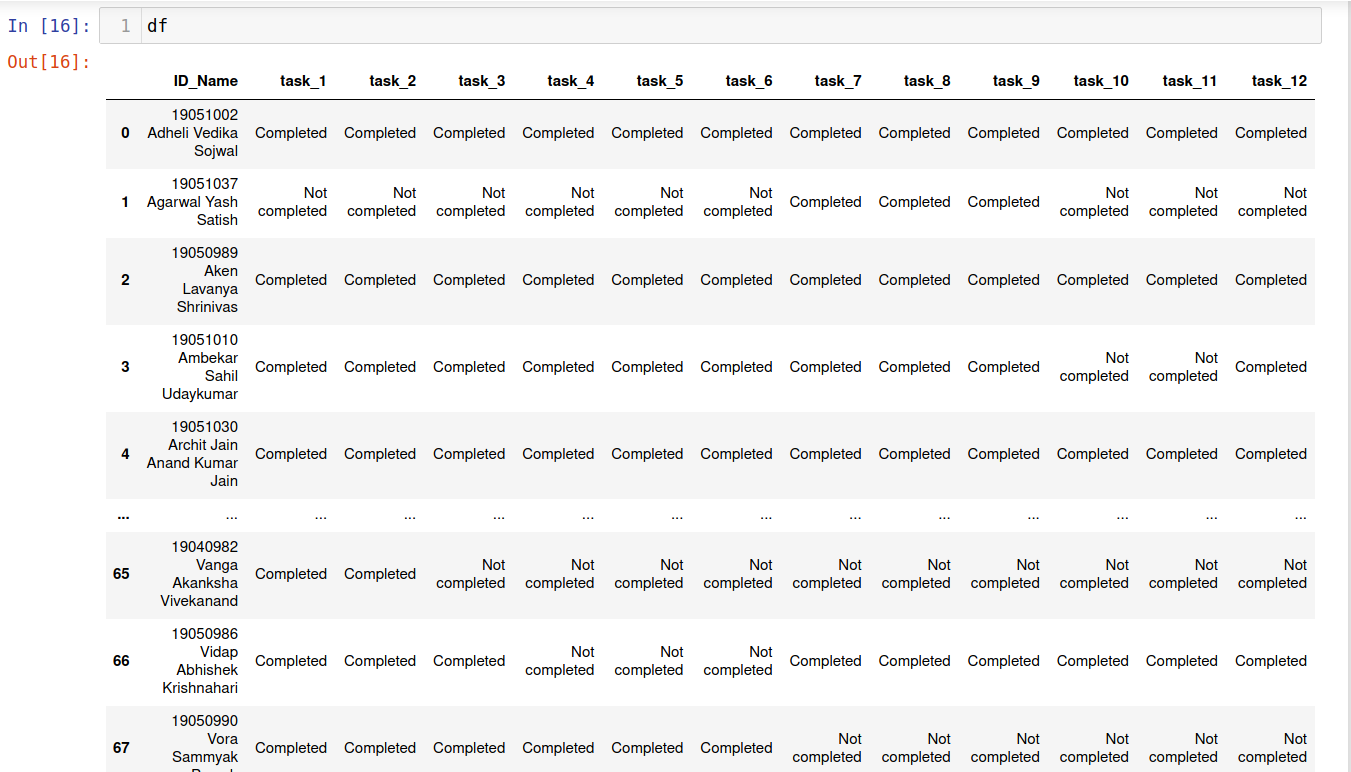
Certainly the column names are much longer, so let us make them something like task_i where i is a number from 1 to 12. To do the same we will use following code.
cols = df.columns.to_list()
df.columns = cols[0::-1] +['task_'+str(i) for i in range(1,13)]
In the above code, we have taken all the column names of the dataframe df and converted it to the list. Since, we need to change all the names of the columns except first column i.e., ID_Name we do this using cols[0::-1]+['task_'+str(i) for i in range(1,13)] where we add two lists [‘ID_Name’] and [‘task_1’,…,’task_12’] and assign the resulting list of column names to df.columns. The resulting dataframe df now looks as follows:
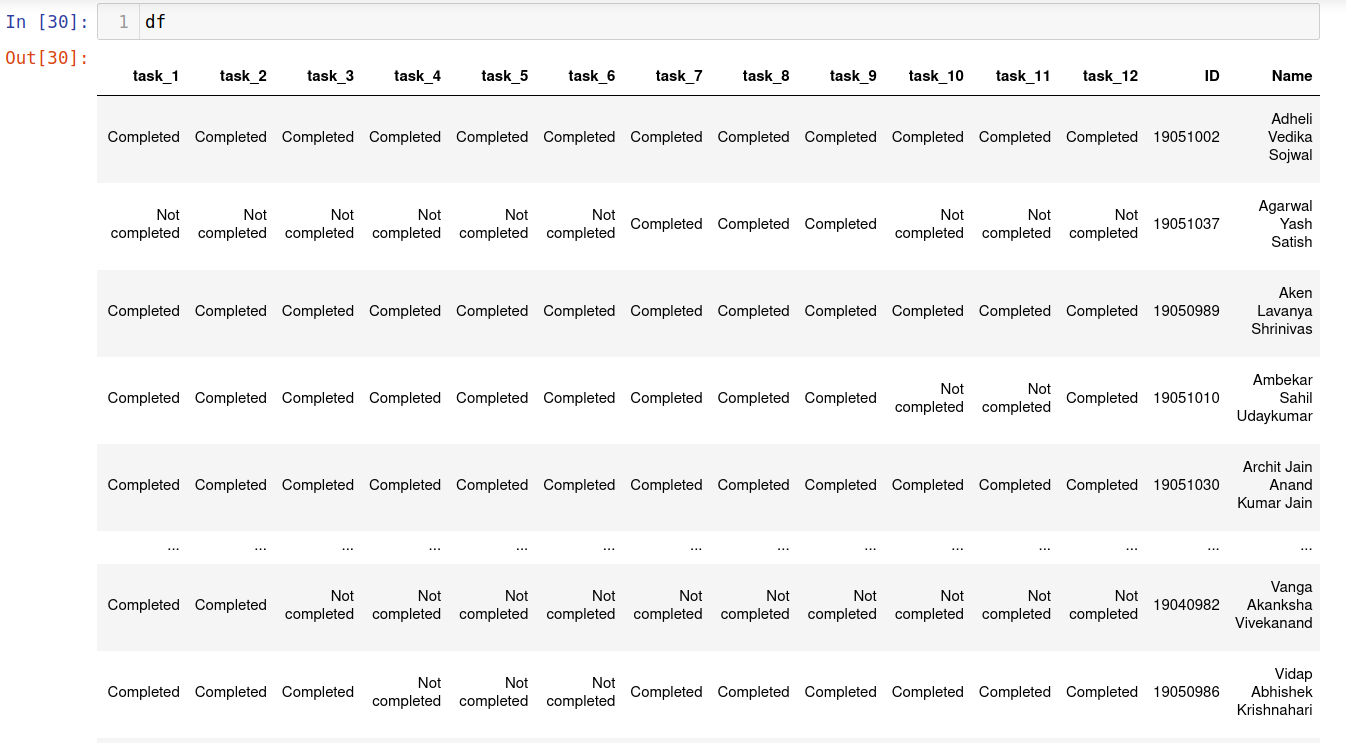
Now let us split the column ID_Name into two seperate columns ID and Name.
To achieve the same, we will use Series.apply() function. Series.apply() function requires function as an argument, so for that let us write two custom functions as follows to get ID and Name for any value in column ID_Name.
def getID(x):
'''
This function will extract the ID from the string x.
The string x is of the form "ID FirstName MiddleName LastName"
'''
l = x.split()
return l[0]
def getName(x):
'''
This function will extract the name from the string x.
The string x is of the form "ID FirstName MiddleName LastName"
'''
l = x.split()
return ' '.join(l[1:])
To get the two new columns from ID_Name column, we write following two lines
df['ID'] = df['ID_Name'].apply(getID)
df['Name'] = df['ID_Name'].apply(getName)
The above lines will create two new columns ID and Name which will be appended after last column of the dataframe df. The df now is:
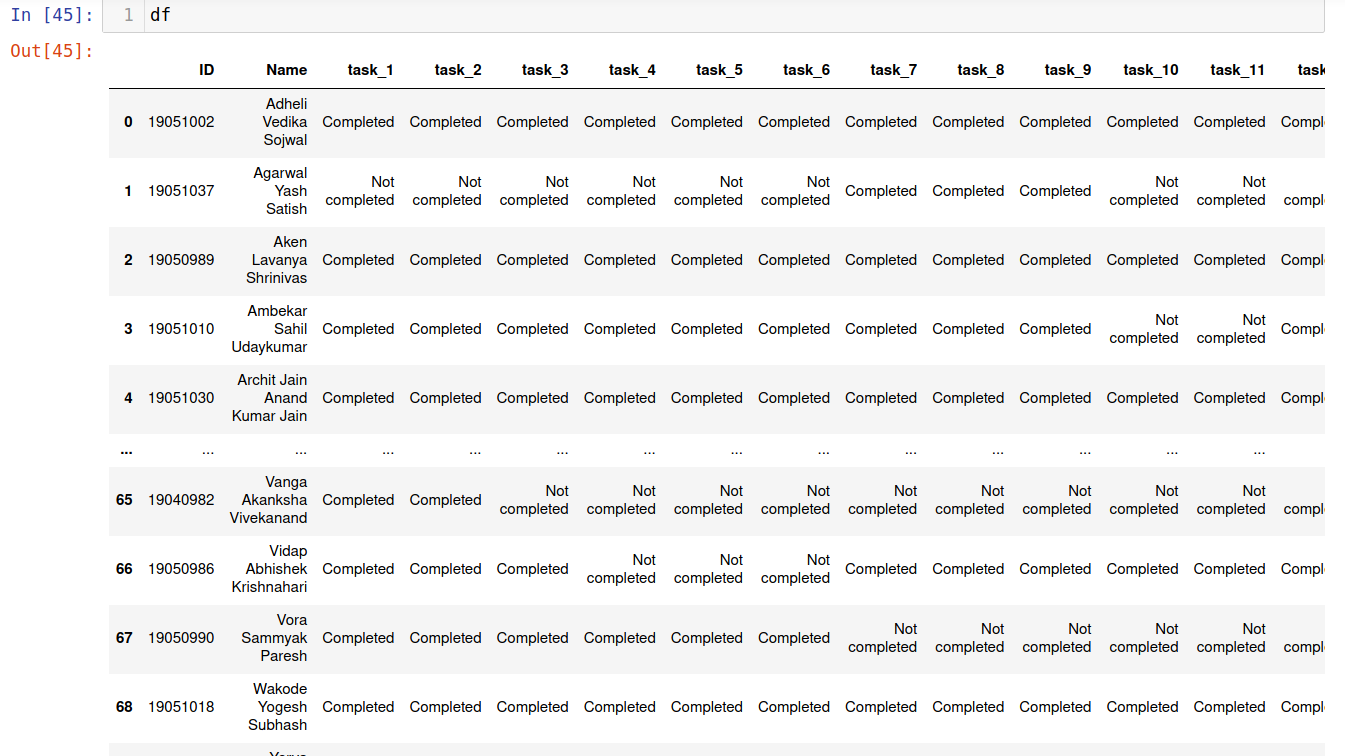
Now let us drop the first column ID_Name and shift last two columns to the front using
# Let us drop the 'ID_Name column'
df = df.drop('ID_Name',axis=1)
# Let us get new column order
new_col_order = df.columns[-2:].to_list() + df.columns[0:-2].to_list()
# get new df with desired column order
df = df[new_col_order]
The new df is
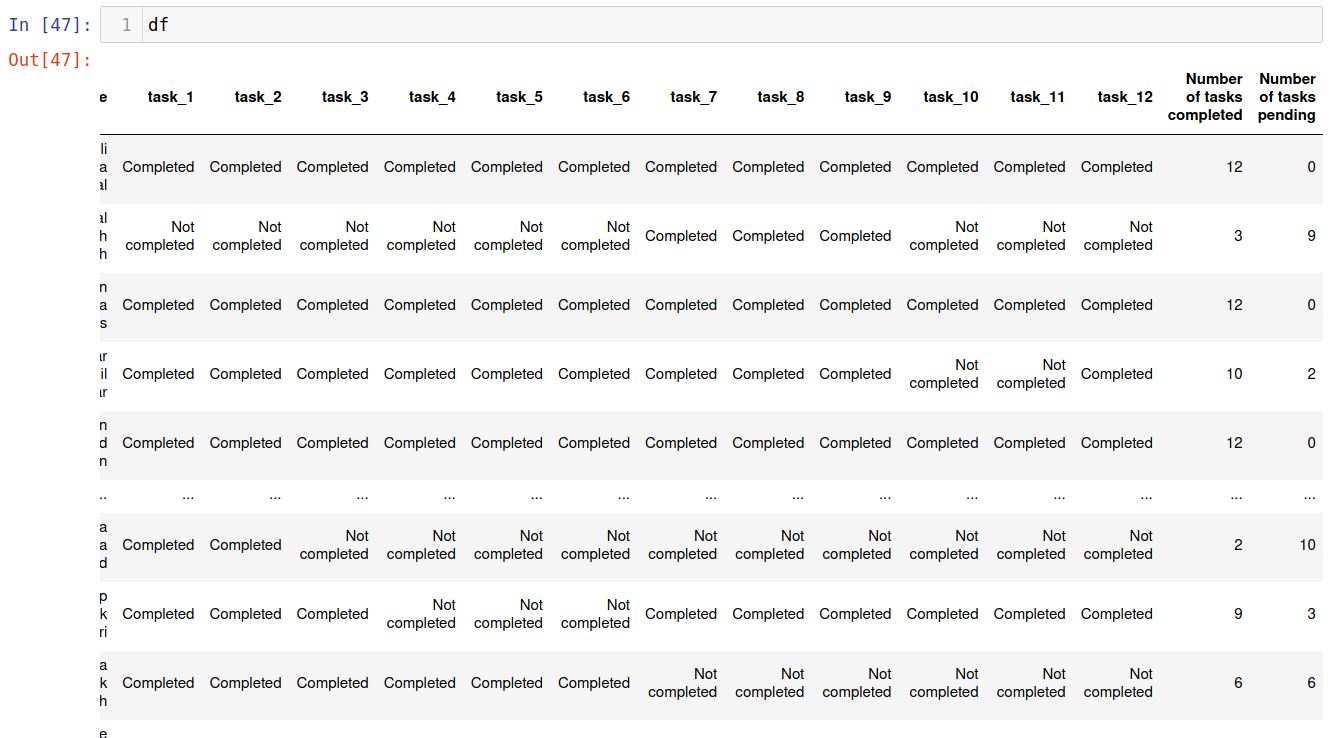
Now, let us create two columns namely “Number of tasks completed” and ‘‘Number of tasks pending’’ showing how many tasks a student has completed and how many are remaining, respectively
To do this we use DataFrame.apply() function as follows.
df['Number of tasks completed'] = df.apply(lambda x: x[x=='Completed'].count(), axis=1)
df['Number of tasks pending'] = df.apply(lambda x: x[x=='Not completed'].count(), axis=1)
The final df is now as follows:
Use of pandas.Series.apply() and pandas.DataFrame.apply() functions is very useful for processing Series and DataFrame objects of pandas library.